GOHIBIC significantly improved survival among patients with COVID-19 receiving IMV and SOC
GOHIBIC caused a reduction in all-cause relative mortality by 23.9% at 28 days1-3
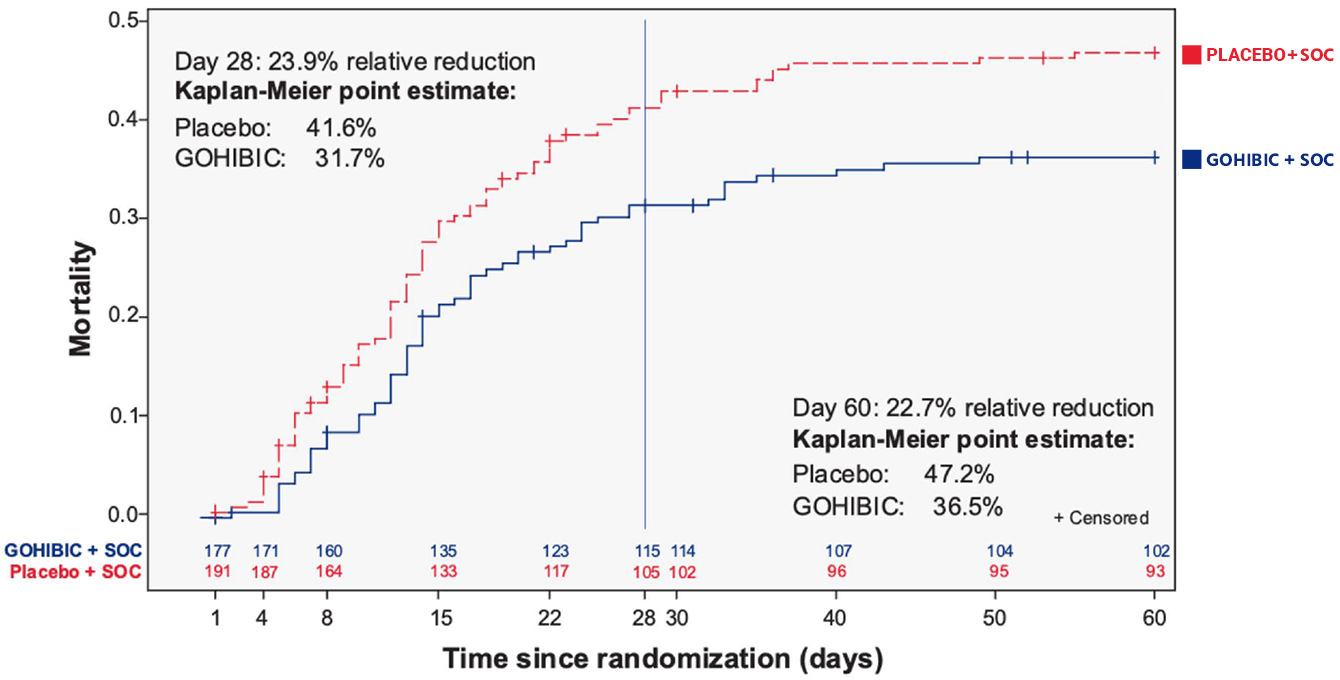
- GOHIBIC + SOC significantly reduced mortality at 28 days compared with placebo + SOC among critically ill patients with COVID-19 who were on IMV or ECMO (HR=0.67 [95% Cl 0.48, 0.96]; P<0.05)1-3
- Results at day 60 were similar1,2
- SOC included concomitant use of corticosteroids (99% of patients), anticoagulants (98%), and immunomodulatory therapies including tocilizumab or baricitinib (~20%)1,2
PANAMO primary endpoint: The Kaplan-Meier estimated 28-day mortality rate in the GOHIBIC group was 31.7% and in the placebo group 41.6%, resulting in a hazard ratio of O.67 (95% Cl 0.48, 0.96; P<0.05).1*
The PANAMO study is the largest known, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial in critically ill, invasively mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 that measured mortality as the primary outcome.2
PANAMO STUDY DESIGN1,2:
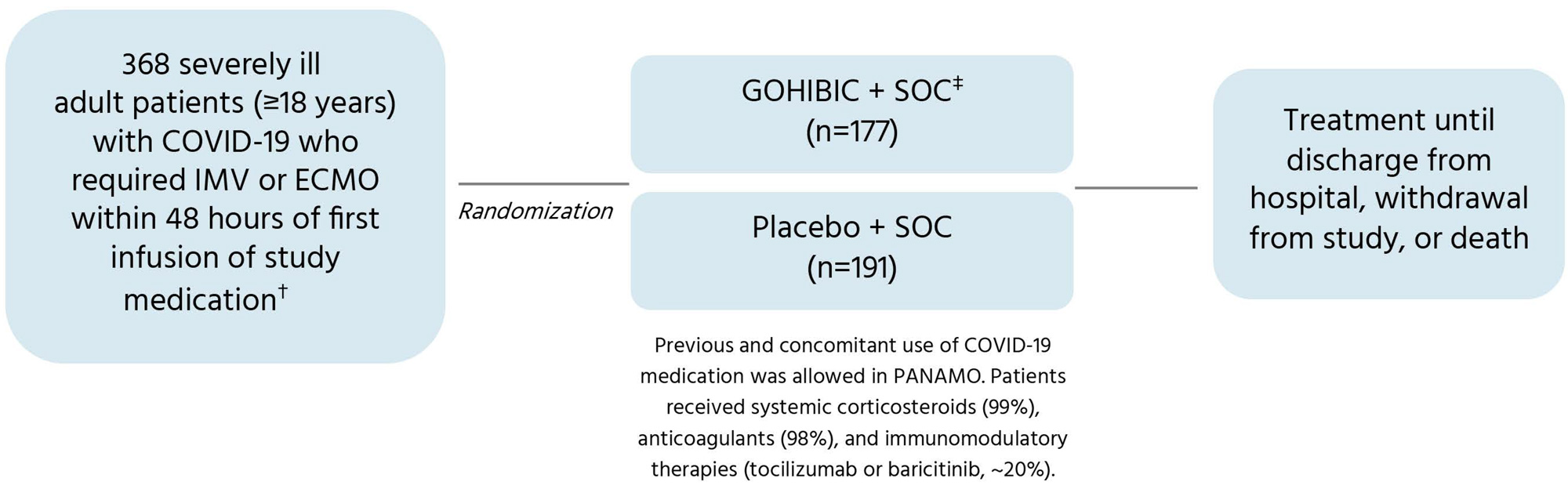
*
Based on a post hoc analysis that used a Cox proportional hazards model without site stratification, which included all randomized patients, the estimated HR demonstrated a statistically significant difference from SOC.3
†
A total of 369 patients were randomized to GOHIBIC + SOC (n=178) or placebo + SOC (n=191). One patient in the GOHIBIC group was randomized in error and not included in the efficacy analyses.1,2
‡
While in the ICU and during hospital stay, patients received SOC and GOHIBIC at a dose of 800 mg IV for a maximum of 6 doses (on days 1, 2, 4, 8, 15, and 22) or a matching placebo. Standard of care at participating sites consisted of intensive care therapy according to current guidelines of each country, including lung protective ventilation, thrombosis prophylaxis, and renal replacement therapy when indicated; COVID-19 medication, including use of corticosteroids, anticoagulants, and biologics or other anti-inflammatory drugs; and access to advanced therapies, including ECMO. Median age was 56 years; 68.5% of patients were male.1,2
Cl, confidence interval; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; HR, hazard ratio; IMV, invasive mechanical ventilation, SOC, standard of care.
Contact us
If you have questions about GOHIBIC, please contact InflaRx via phone or email.
Phone: 1-888-254-0602
General Inquiries: Info.Gohibic@inflarx.com
Medical Inquiries: medinfo@inflarx.com
AUTHORIZED USE FOR GOHIBIC
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the use of GOHIBIC® (vilobelimab) for the treatment of COVID‑19 in hospitalized adults when initiated within 48 hours of receiving IMV or ECMO. GOHIBIC is not FDA approved for this use.1
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Contraindications: No contraindications have been identified based on limited available data on emergency use of GOHIBIC authorized under this EUA.
Warnings and Precautions: There are limited clinical data available for GOHIBIC. Serious and unexpected adverse events (AEs) may occur that have not been previously reported with GOHIBIC use.
Serious Infections: Serious infections due to bacterial, fungal, and viral pathogens have been reported in patients with COVID‑19 receiving GOHIBIC. In patients with COVID‑19, monitor for signs and symptoms of new infections during and after treatment with GOHIBIC. There is limited information regarding the use of GOHIBIC in patients with COVID‑19 and concomitant active serious infections. The risks and benefits of treatment with GOHIBIC in COVID‑19 patients with other concurrent infections should be considered.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions have been observed with GOHIBIC. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction occurs, administration of GOHIBIC should be discontinued and appropriate therapy initiated.
Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions (adverse events reported with incidence ≥3% and >1% more commonly observed than in the placebo arm) are pneumonia, sepsis, delirium, pulmonary embolism, hypertension, pneumothorax, deep vein thrombosis, herpes simplex, enterococcal infection, bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, hepatic enzyme increased, urinary tract infection, hypoxia, thrombocytopenia, pneumomediastinum, respiratory tract infection, supraventricular tachycardia, constipation, and rash.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
There are no available data on GOHIBIC use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Placental transfer of monoclonal antibodies such as GOHIBIC is greater during the third trimester of pregnancy; therefore, potential effects on a fetus are likely to be greater during the third trimester of pregnancy. In an enhanced pre- and post-natal (ePPND) study conducted in cynomolgus monkeys, placental transport of GOHIBIC was observed but there was no evidence of fetal harm following intravenous administration of GOHIBIC throughout pregnancy at doses 2.5 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 800 mg on a mg/kg basis (see Data). The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the US general population, the estimated background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage in clinical recognized pregnancies are 2%–4% and 15%–20%, respectively.
Pediatric Use
GOHIBIC is not authorized or approved for the emergency use in pediatric patients for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19) in hospitalized patients when initiated within 48 hours of receiving invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of GOHIBIC-treated patients in clinical studies for COVID‑19 receiving invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), 53 (30%) were >65 years. No overall differences in effectiveness or safety of GOHIBIC have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients.
For additional information, please see:
Required Reporting for Serious Adverse Events and Medication Errors
The prescribing healthcare provider and/or the provider’s designee is/are responsible for mandatory reporting of all serious adverse events (SAEs) and medication errors potentially related to GOHIBIC within 7 calendar days from the healthcare provider’s awareness of the event.
To report adverse events and medication errors, complete and submit FDA Form 3500 to MedWatch online at https://www.fda.gov/medwatch/report.htm, or download FDA Form 3500 at https://www.fda.gov/media/76299/download and mail the completed form to MedWatch at 5600 Fishers Lane, Rockville, MD 20852-9787 or fax it to 1-800-FDA-0178. You may also request a reporting form by calling 1-800-FDA-1088.
In addition, please provide a copy of all FDA MedWatch forms to:
InflaRx GmbH Fax: 1-866-728-2630 Email: pvusa@inflarx.de, or call InflaRx GmbH at 1-888-254-0602 to report AEs.
IMPORTANT TO NOTE: Submitted reports must state, “GOHIBIC use for COVID‑19 under Emergency Use Authorization” at the beginning of the question “Describe Event” for further analysis. A copy of the completed FDA Form 3500 must also be provided to InflaRx per the instructions in the authorized labeling.
References: 1. GOHIBIC Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers, InflaRx GmbH. May 2023. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/media/166824/download. 2. Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for Vilobelimab Letter of Authorization InflaRx GmbH. April 2023. Available at: EUA 118 InflaRx GOHIBIC LOA (04122023) (fda.gov). 3. GOHIBIC Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers, InflaRx GmbH. April 2023. Available at https://www.fda.gov/media/166821/download.